快速入门
本指南将逐步引导您完成在 Electron 中创建基本 Hello World 应用程序的过程,类似于 electron/electron-quick-start。
在本教程结束时,您的应用程序将打开一个浏览器窗口,其中显示一个网页,其中包含有关正在运行的 Chromium、Node.js 和 Electron 版本的信息。
先决条件
要使用 Electron,您需要安装 Node.js。我们建议您使用最新的 LTS 版本。
请使用针对您的平台的预构建安装程序安装 Node.js。否则,您可能会遇到与不同开发工具的不兼容问题。
要检查 Node.js 是否已正确安装,请在您的终端客户端中键入以下命令
node -v
npm -v
这些命令应分别打印 Node.js 和 npm 的版本。
注意:由于 Electron 将 Node.js 嵌入到其二进制文件中,因此运行代码的 Node.js 版本与系统上运行的版本无关。
创建您的应用程序
搭建项目
Electron 应用程序的总体结构与其他 Node.js 项目相同。首先创建一个文件夹并初始化一个 npm 包。
- npm
- Yarn
mkdir my-electron-app && cd my-electron-app
npm init
mkdir my-electron-app && cd my-electron-app
yarn init
交互式 init 命令将提示您在配置中设置一些字段。为了本教程的目的,有一些规则需要遵循
入口点应为main.js。作者和描述可以是任何值,但对于 应用程序打包是必需的。
您的 package.json 文件应如下所示
{
"name": "my-electron-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Hello World!",
"main": "main.js",
"author": "Jane Doe",
"license": "MIT"
}
然后,将 electron 包安装到您的应用程序的 devDependencies 中。
- npm
- Yarn
npm install --save-dev electron
yarn add --dev electron
注意:如果您在安装 Electron 时遇到任何问题,请参阅高级安装指南。
最后,您希望能够执行 Electron。在您的 package.json 配置的 scripts 字段中,添加一个 start 命令,如下所示
{
"scripts": {
"start": "electron ."
}
}
此 start 命令将允许您在开发模式下打开您的应用程序。
- npm
- Yarn
npm start
yarn start
注意:此脚本告诉 Electron 在您的项目根文件夹中运行。在此阶段,您的应用程序会立即抛出一个错误,告诉您它找不到要运行的应用程序。
运行主进程
任何 Electron 应用程序的入口点是其 main 脚本。此脚本控制主进程,该进程在完整的 Node.js 环境中运行,负责控制应用程序的生命周期、显示本机界面、执行特权操作以及管理渲染器进程(稍后会详细介绍)。
在执行期间,Electron 将在应用程序的 package.json 配置的 main 字段中查找此脚本,您应该在应用程序搭建步骤中配置它。
要初始化 main 脚本,请在项目的根文件夹中创建一个名为 main.js 的空文件。
注意:如果您此时再次运行
start脚本,您的应用程序将不再抛出任何错误!但是,它不会执行任何操作,因为我们尚未在main.js中添加任何代码。
创建网页
在我们可以为我们的应用程序创建一个窗口之前,我们需要创建将加载到其中的内容。在 Electron 中,每个窗口都显示可以从本地 HTML 文件或远程 URL 加载的 Web 内容。
在本教程中,您将执行前者。在您的项目的根文件夹中创建一个 index.html 文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- https://mdn.org.cn/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP -->
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src 'self'; script-src 'self'">
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
We are using Node.js <span id="node-version"></span>,
Chromium <span id="chrome-version"></span>,
and Electron <span id="electron-version"></span>.
</body>
</html>
注意:查看此 HTML 文档,您可以观察到正文文本中缺少版本号。我们稍后将使用 JavaScript 手动插入它们。
在浏览器窗口中打开您的网页
现在您有了一个网页,请将其加载到应用程序窗口中。为此,您需要两个 Electron 模块
app模块,用于控制应用程序的事件生命周期。BrowserWindow模块,用于创建和管理应用程序窗口。
由于主进程运行 Node.js,您可以将它们作为 CommonJS 模块导入到您的 main.js 文件的顶部
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron')
然后,添加一个 createWindow() 函数,该函数将 index.html 加载到新的 BrowserWindow 实例中。
const createWindow = () => {
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600
})
win.loadFile('index.html')
}
接下来,调用此 createWindow() 函数以打开您的窗口。
在 Electron 中,只有在 app 模块的 ready 事件触发后才能创建浏览器窗口。您可以使用 app.whenReady() API 等待此事件。在 whenReady() 解析其 Promise 之后调用 createWindow()。
app.whenReady().then(() => {
createWindow()
})
注意:此时,您的 Electron 应用程序应该成功打开一个显示您的网页的窗口!
管理窗口的生命周期
虽然您现在可以打开浏览器窗口,但您还需要一些额外的样板代码才能使其在每个平台上感觉更原生。应用程序窗口在每个操作系统上的行为都不同,Electron 将在应用程序中实现这些约定的责任交给开发人员。
通常,您可以使用 process 全局变量的 platform 属性来专门为某些操作系统运行代码。
当所有窗口关闭时退出应用程序(Windows 和 Linux)
在 Windows 和 Linux 上,退出所有窗口通常会完全退出应用程序。
要实现此目的,请监听 app 模块的 'window-all-closed' 事件,如果用户不是在 macOS (darwin) 上,则调用 app.quit()。
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {
if (process.platform !== 'darwin') app.quit()
})
如果没有打开任何窗口,则打开一个窗口 (macOS)
Linux 和 Windows 应用程序在没有打开窗口时会退出,而 macOS 应用程序通常即使没有任何打开的窗口也会继续运行,并且在没有窗口可用时激活该应用程序应打开一个新窗口。
要实现此功能,请监听 app 模块的 activate 事件,如果没有打开任何浏览器窗口,则调用您现有的 createWindow() 方法。
由于无法在 ready 事件之前创建窗口,因此您应该仅在初始化应用程序后监听 activate 事件。通过从现有的 whenReady() 回调中附加事件侦听器来执行此操作。
app.whenReady().then(() => {
createWindow()
app.on('activate', () => {
if (BrowserWindow.getAllWindows().length === 0) createWindow()
})
})
注意:此时,您的窗口控件应完全正常运行!
使用预加载脚本从渲染器访问 Node.js
现在,最后要做的是将 Electron 及其依赖项的版本号打印到您的网页上。
通过 Node 的全局 process 对象,在主进程中访问此信息非常简单。但是,您不能直接从主进程编辑 DOM,因为它无法访问渲染器的 document 上下文。它们位于完全不同的进程中!
注意:如果您需要更深入地了解 Electron 进程,请参阅进程模型文档。
这就是将**预加载**脚本附加到您的渲染器的好处。预加载脚本在渲染器进程加载之前运行,并且可以访问渲染器全局变量(例如 window 和 document)和 Node.js 环境。
创建一个名为 preload.js 的新脚本,如下所示
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const replaceText = (selector, text) => {
const element = document.getElementById(selector)
if (element) element.innerText = text
}
for (const dependency of ['chrome', 'node', 'electron']) {
replaceText(`${dependency}-version`, process.versions[dependency])
}
})
上面的代码访问 Node.js process.versions 对象,并运行一个基本的 replaceText 辅助函数,将版本号插入到 HTML 文档中。
要将此脚本附加到您的渲染器进程,请将您的预加载脚本的路径传递给您现有的 BrowserWindow 构造函数中的 webPreferences.preload 选项。
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron')
// include the Node.js 'path' module at the top of your file
const path = require('node:path')
// modify your existing createWindow() function
const createWindow = () => {
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
preload: path.join(__dirname, 'preload.js')
}
})
win.loadFile('index.html')
}
// ...
这里使用了两个 Node.js 概念
我们使用相对于当前正在执行的 JavaScript 文件的路径,以便您的相对路径在开发模式和打包模式下都有效。
奖励:为您的 Web 内容添加功能
此时,您可能想知道如何为您的应用程序添加更多功能。
对于与您的 Web 内容的任何交互,您都希望将脚本添加到您的渲染器进程中。由于渲染器在正常的 Web 环境中运行,因此您可以在 index.html 文件的结束 </body> 标记之前添加 <script> 标记,以包含您想要的任何任意脚本
<script src="./renderer.js"></script>
然后,renderer.js 中包含的代码可以使用您用于典型前端开发的相同 JavaScript API 和工具,例如使用webpack来捆绑和缩小您的代码,或者使用React来管理您的用户界面。
回顾
在完成以上步骤后,您应该拥有一个功能齐全的 Electron 应用程序,如下所示
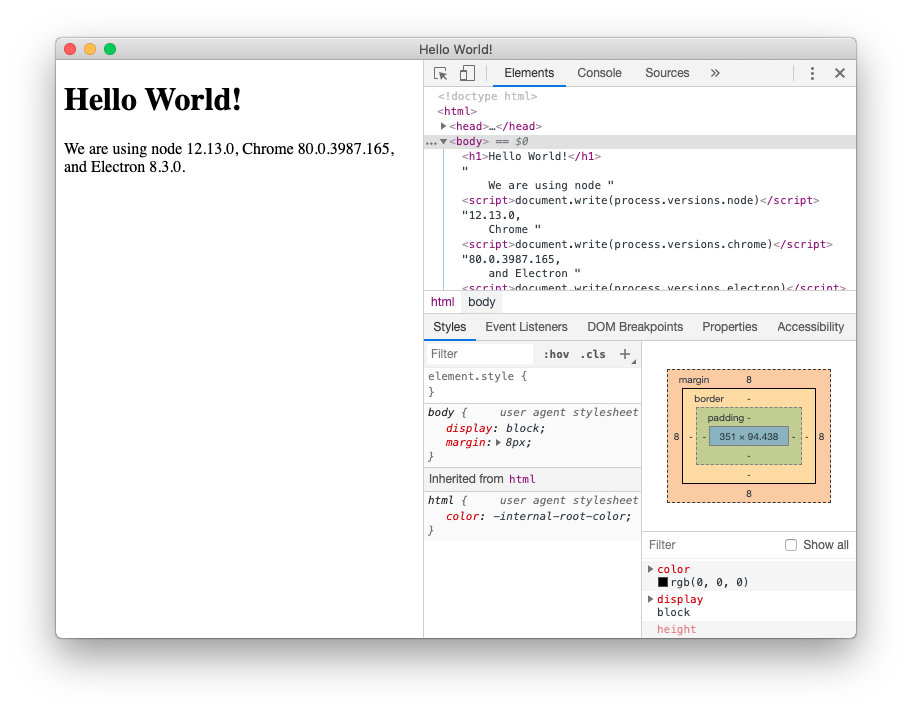
完整代码如下
// main.js
// Modules to control application life and create native browser window
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron')
const path = require('node:path')
const createWindow = () => {
// Create the browser window.
const mainWindow = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
preload: path.join(__dirname, 'preload.js')
}
})
// and load the index.html of the app.
mainWindow.loadFile('index.html')
// Open the DevTools.
// mainWindow.webContents.openDevTools()
}
// This method will be called when Electron has finished
// initialization and is ready to create browser windows.
// Some APIs can only be used after this event occurs.
app.whenReady().then(() => {
createWindow()
app.on('activate', () => {
// On macOS it's common to re-create a window in the app when the
// dock icon is clicked and there are no other windows open.
if (BrowserWindow.getAllWindows().length === 0) createWindow()
})
})
// Quit when all windows are closed, except on macOS. There, it's common
// for applications and their menu bar to stay active until the user quits
// explicitly with Cmd + Q.
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {
if (process.platform !== 'darwin') app.quit()
})
// In this file you can include the rest of your app's specific main process
// code. You can also put them in separate files and require them here.
// preload.js
// All the Node.js APIs are available in the preload process.
// It has the same sandbox as a Chrome extension.
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const replaceText = (selector, text) => {
const element = document.getElementById(selector)
if (element) element.innerText = text
}
for (const dependency of ['chrome', 'node', 'electron']) {
replaceText(`${dependency}-version`, process.versions[dependency])
}
})
<!--index.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- https://mdn.org.cn/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP -->
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src 'self'; script-src 'self'">
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
We are using Node.js <span id="node-version"></span>,
Chromium <span id="chrome-version"></span>,
and Electron <span id="electron-version"></span>.
<!-- You can also require other files to run in this process -->
<script src="./renderer.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
- main.js
- preload.js
- index.html
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron/main')
const path = require('node:path')
function createWindow () {
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
preload: path.join(__dirname, 'preload.js')
}
})
win.loadFile('index.html')
}
app.whenReady().then(() => {
createWindow()
app.on('activate', () => {
if (BrowserWindow.getAllWindows().length === 0) {
createWindow()
}
})
})
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {
if (process.platform !== 'darwin') {
app.quit()
}
})
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const replaceText = (selector, text) => {
const element = document.getElementById(selector)
if (element) element.innerText = text
}
for (const type of ['chrome', 'node', 'electron']) {
replaceText(`${type}-version`, process.versions[type])
}
})
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hello World!</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline';" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>
We are using Node.js <span id="node-version"></span>,
Chromium <span id="chrome-version"></span>,
and Electron <span id="electron-version"></span>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
总结一下我们所做的所有步骤
- 我们引导了一个 Node.js 应用程序,并添加了 Electron 作为依赖项。
- 我们创建了一个
main.js脚本,该脚本运行我们的主进程,该进程控制我们的应用程序并在 Node.js 环境中运行。在此脚本中,我们使用 Electron 的app和BrowserWindow模块创建一个浏览器窗口,该窗口在单独的进程(渲染器)中显示 Web 内容。 - 为了在渲染器中访问某些 Node.js 功能,我们将一个预加载脚本附加到我们的
BrowserWindow构造函数。
打包并分发您的应用程序
分发您新创建的应用程序的最快方法是使用Electron Forge。
要为 Linux 构建 RPM 包,您需要安装其所需的系统依赖项。
-
在您的
package.json文件中添加描述,否则 rpmbuild 将失败。空白描述无效。 -
将 Electron Forge 添加为您的应用程序的开发依赖项,并使用其
import命令来设置 Forge 的脚手架- npm
- Yarn
npm install --save-dev @electron-forge/cli
npx electron-forge import
✔ Checking your system
✔ Initializing Git Repository
✔ Writing modified package.json file
✔ Installing dependencies
✔ Writing modified package.json file
✔ Fixing .gitignore
We have ATTEMPTED to convert your app to be in a format that electron-forge understands.
Thanks for using "electron-forge"!!!npm install --save-dev @electron-forge/cli
yarn dlx electron-forge import
✔ Checking your system
✔ Initializing Git Repository
✔ Writing modified package.json file
✔ Installing dependencies
✔ Writing modified package.json file
✔ Fixing .gitignore
We have ATTEMPTED to convert your app to be in a format that electron-forge understands.
Thanks for using "electron-forge"!!! -
使用 Forge 的
make命令创建一个可分发文件- npm
- Yarn
npm run make
> my-electron-app@1.0.0 make /my-electron-app
> electron-forge make
✔ Checking your system
✔ Resolving Forge Config
We need to package your application before we can make it
✔ Preparing to Package Application for arch: x64
✔ Preparing native dependencies
✔ Packaging Application
Making for the following targets: zip
✔ Making for target: zip - On platform: darwin - For arch: x64yarn make
> my-electron-app@1.0.0 make /my-electron-app
> electron-forge make
✔ Checking your system
✔ Resolving Forge Config
We need to package your application before we can make it
✔ Preparing to Package Application for arch: x64
✔ Preparing native dependencies
✔ Packaging Application
Making for the following targets: zip
✔ Making for target: zip - On platform: darwin - For arch: x64Electron Forge 创建
out文件夹,您的软件包将位于该文件夹中// Example for macOS
out/
├── out/make/zip/darwin/x64/my-electron-app-darwin-x64-1.0.0.zip
├── ...
└── out/my-electron-app-darwin-x64/my-electron-app.app/Contents/MacOS/my-electron-app